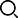Analysis of the Causes of Engine Crankshaft Fracture
Release time:
2021-01-05
Main reasons for crankshaft fracture:
(1) Some users have chosen inappropriate engine oil or neglected the cleaning and replacement of the 'three filters', leading to long-term deterioration of the oil; severe overload and over-towing cause the engine to operate under excessive load for a long time, resulting in bearing burning incidents. Due to bearing burning, the crankshaft suffers severe wear. The WD615 series engine crankshaft is repaired by replacing it with a new one while sending the damaged crankshaft back to the manufacturer for repair as a backup. Some users, after encountering crankshaft wear issues, consider costs and time and seek local small factories for repairs, where severely worn crankshafts are welded, processed, and subjected to overall heat treatment followed by grinding. Due to issues with repair methods and processes, changes occur in the connection fillet between the crank pin and main journal with the crank arm, causing localized stress concentration; since the crankshaft is forged from precision 45 steel, welding also alters its metallographic structure. These two factors are the main reasons for crankshaft fractures.
(2) After repairing the engine, if it is installed without going through a break-in period and is overloaded or over-towed, it causes long-term excessive load operation of the engine, exceeding permissible limits on the crankshaft.
(3) During crankshaft repair using welding techniques that disrupt its dynamic balance without performing balance checks leads to excessive imbalance levels, causing significant vibrations in the engine that result in crankshaft fractures.
(4) Due to poor road conditions combined with severe overload and over-towing of vehicles, if engines frequently operate within critical torsional vibration speeds while dampers fail, this can also lead to torsional vibration fatigue damage resulting in fractures of the crankshaft.
Latest News