Research on the Fatigue Performance Analysis of Engine Crankshafts You Don't Know About
Release time:
2020-11-19
The crankshaft is an important component of the automobile engine. Whether in the research and development of automobile crankshafts or in the actual production stage, it is necessary to test the fatigue performance of automobile crankshafts.
The crankshaft is an important component of the automobile engine. Whether in the research and development or actual production phase of the automobile crankshaft, it is necessary to test the fatigue performance of the crankshaft. During the actual operation of the automobile engine, the loads that the crankshaft must bear are bending and torsional loads. Therefore, practical cases show that the main failure mode of automobile crankshafts is bending fatigue failure.
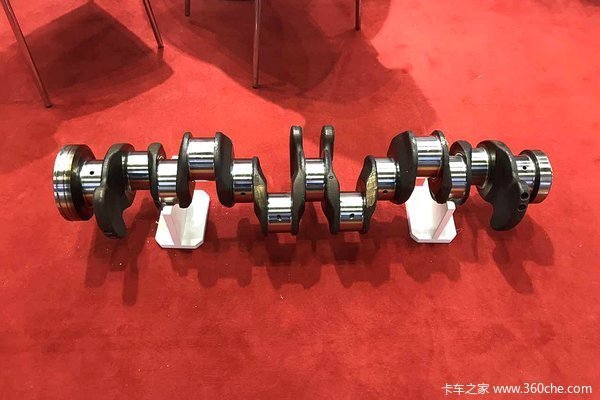

Additionally, if the output power of the engine crankshaft is large and generates significant torque, it will lead to a certain degree of torsional fatigue failure. The materials used for early automobile engine crankshafts were medium carbon alloy steels such as 40Cr and 42CrMo.
However, since the late 1990s, a large number of automobile crankshafts have begun to widely use non-alloy steel, especially for heavy-duty vehicle engine crankshafts. The materials mainly include 48MnV and C38N2, which omit many quenching processes while ensuring similar strength compared to medium carbon alloy steel.
In recent years, automobile crankshafts produced from ductile iron have shown better machinability and bending fatigue strength, especially demonstrating good application prospects in heavy-load engines.
In every aspect of designing, selecting raw materials, forging, machining, heat treatment, and surface hardening of automobile crankshafts, any mistake in any link can lead to failure of the crankshaft. A certain company has introduced and analyzed common failure modes and intrinsic reasons for automobile engine crankshafts based on actual bearing production cases.
Currently, factors affecting the fatigue strength of automobile crankshafts mainly include stress concentration at part journal locations, dimensions, surface conditions, and environmental media. Among these factors, stress concentration along with dimensions and surface conditions are most important.
Factors affecting stress distribution in a crankshaft mainly include its design shape and basic material properties. The bending fatigue strength can be improved by changing material types as well as dimensions; however, this significantly increases manufacturing costs.
In practical applications, surface hardening processes are usually employed to improve fatigue strength. Under variable loads on an automobile crankshaft due to sudden changes in shape at journal locations; thus maximum stress should occur within a range near the fillet radius at journal ends. Research results indicate:
(1) In fatigue tests on automotive crankshafts with a cycle base of 1×10^7 times: The bending moment's fatigue limit is 607.5Nm; The fatigue limit pressure at mid-journal is 96.7MPa; The stress concentration factor for the shaft is 6.72; The safety factor when survival rate during testing is at 99% is 1.31.
(2) From metallographic analysis and SEM analysis of cracks at journal locations on a 40Cr shaft: After quenching treatment on this material shows microstructure consisting of tempered sorbite + ferrite + minor bainite which meets relevant standards. Fracture analysis indicates that this fracture features typical ductile dimples mixed with step-like fractures without obvious inclusions.
(3) Analysis from chemical composition and tensile properties along with hardened layers on journal surfaces indicates that these factors can be ruled out as causes for shaft fatigue fracture.
(4) Stress concentration caused by oil drilling holes on inner walls leads to defects more easily; under alternating stresses at journal locations it’s easy for cracks to initiate leading to early fracture.
All content above comes from online sources; if there are any issues please contact me for deletion.
Latest News